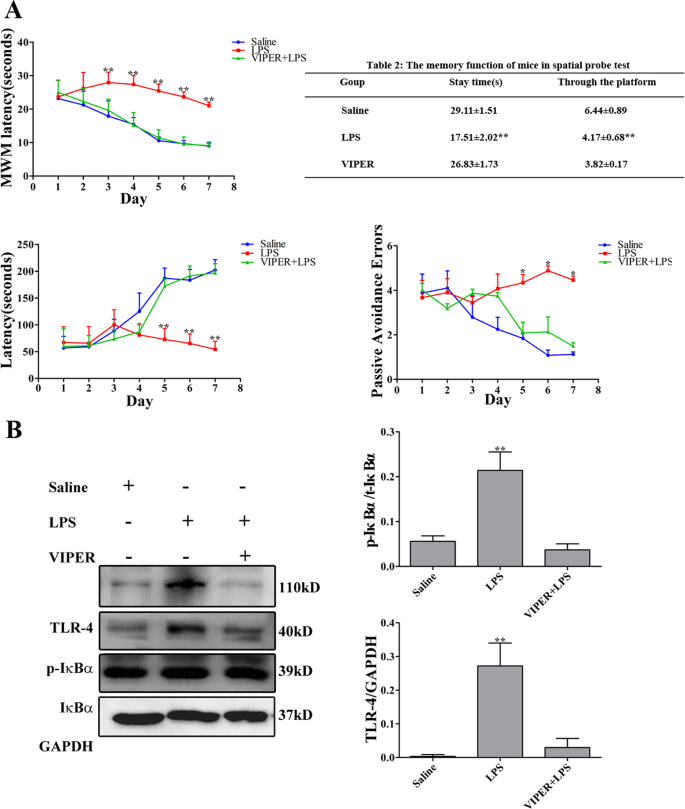
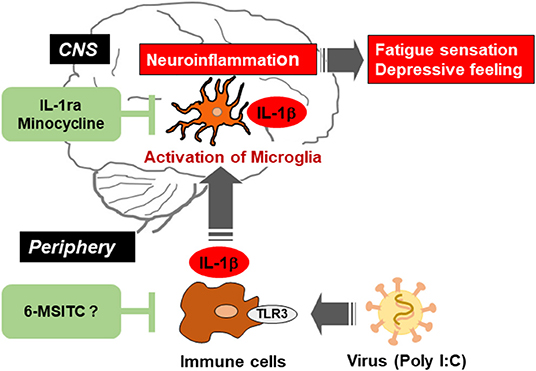
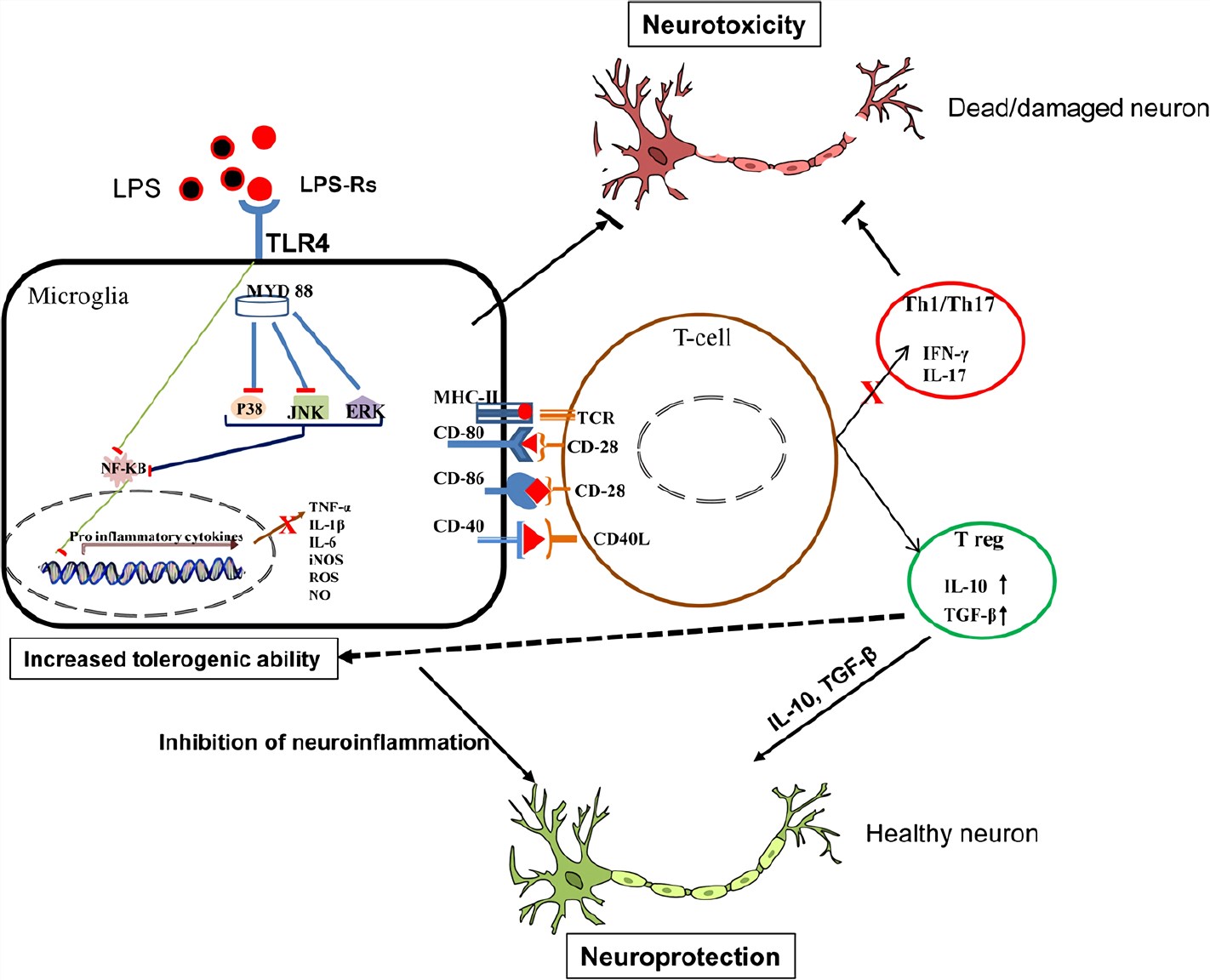
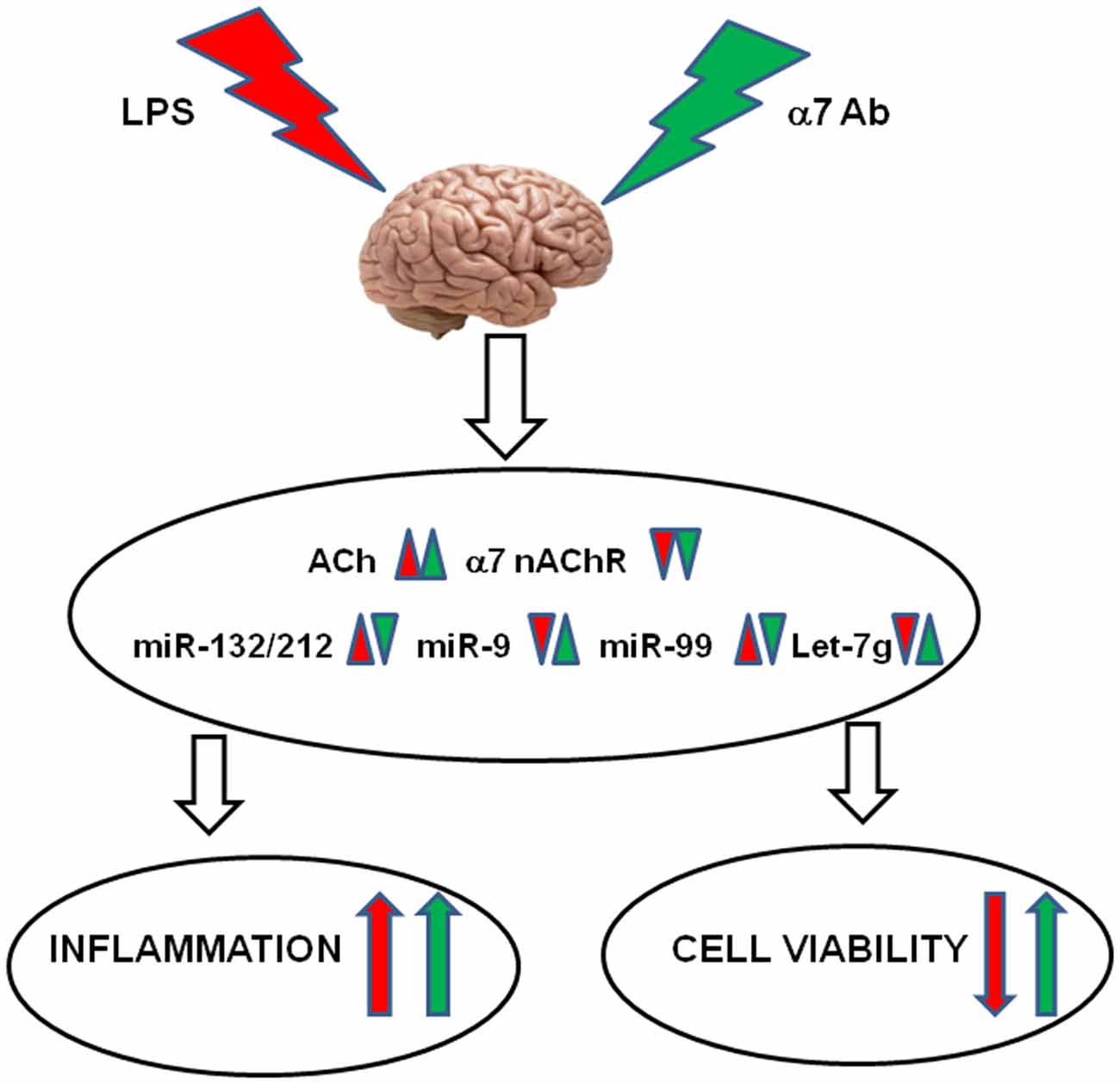
Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates LPS-induced cognitive impairments and neuroinflammation by inhibiting NOX2 and Ca2+–CN–NFAT1 signaling in mice - ScienceDirect

Eriodictyol Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Amyloidogenesis, and Cognitive Impairments via the Inhibition of NF-κB in Male C57BL/6J Mice and BV2 Microglial Cells | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
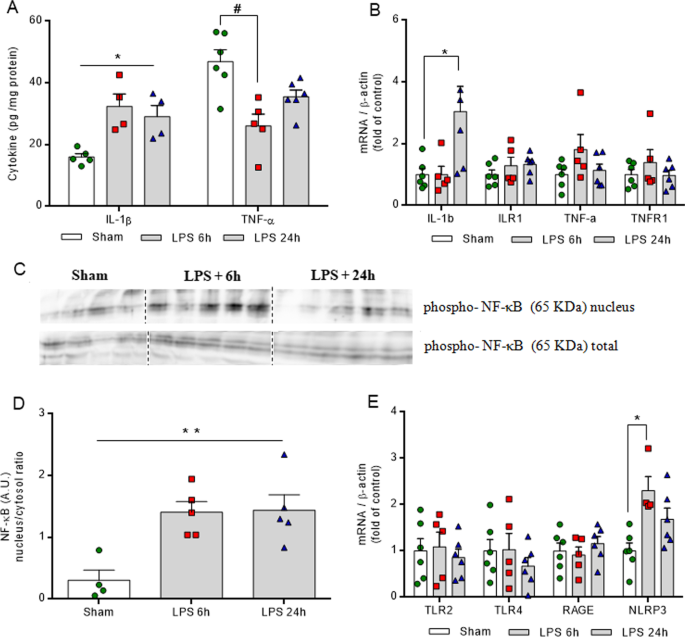
Early effects of LPS-induced neuroinflammation on the rat hippocampal glycolytic pathway | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Systemic inflammation induced the delayed reduction of excitatory synapses in the CA3 during ageing - Manabe - 2021 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Hesperetin, a Citrus Flavonoid, Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Memory Impairments by Modulating TLR4/NF-κB Signaling

Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide induced model of Parkinson's disease: Role of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation - ScienceDirect

IL-33 and ST2 expression in the brain after LPS stimulation. I.c.v. LPS... | Download Scientific Diagram

Lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation induces presynaptic disruption through a direct action on brain tissue involving microglia-derived interleukin 1 beta | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text
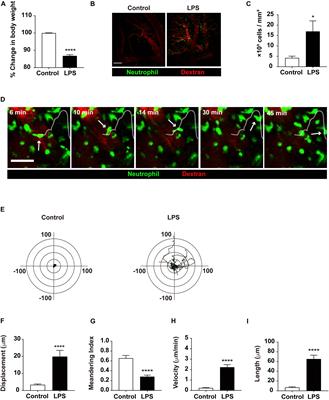
Frontiers | Neutrophils Return to Bloodstream Through the Brain Blood Vessel After Crosstalk With Microglia During LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation
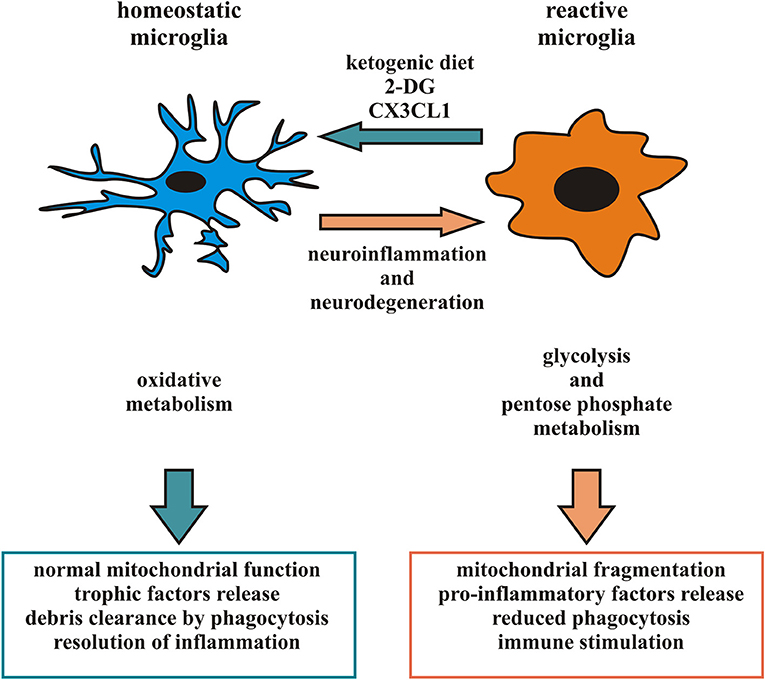
Frontiers | Metabolic Reprograming of Microglia in the Regulation of the Innate Inflammatory Response

Fenretinide attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced blood-brain barrier (BBB) and depressive-like behavior in mice by targeting Nrf-2 signaling - ScienceDirect

Molecular and functional properties of cortical astrocytes during peripherally induced neuroinflammation - ScienceDirect
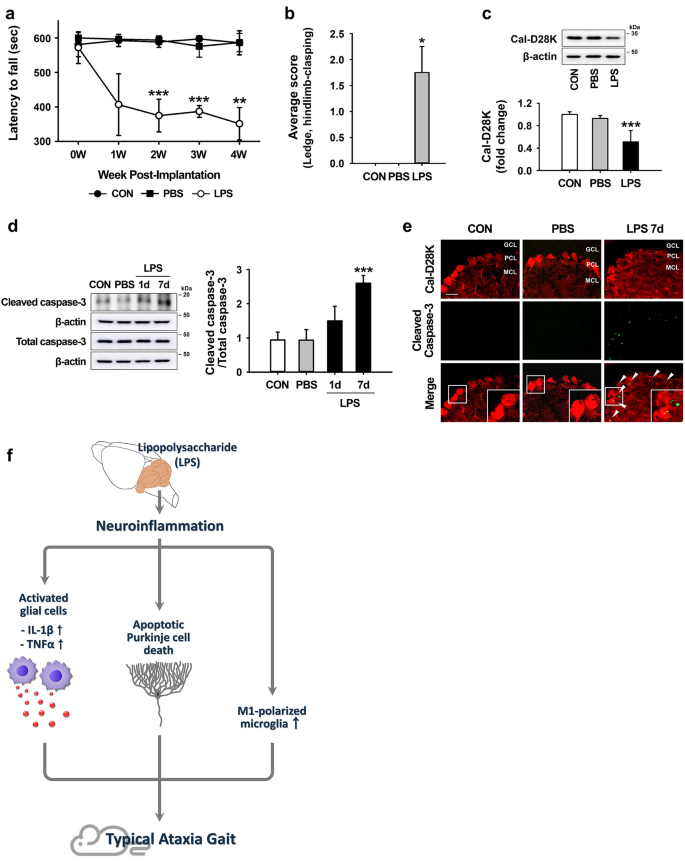
Lipopolysaccharide administration for a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia with neuroinflammation | Scientific Reports
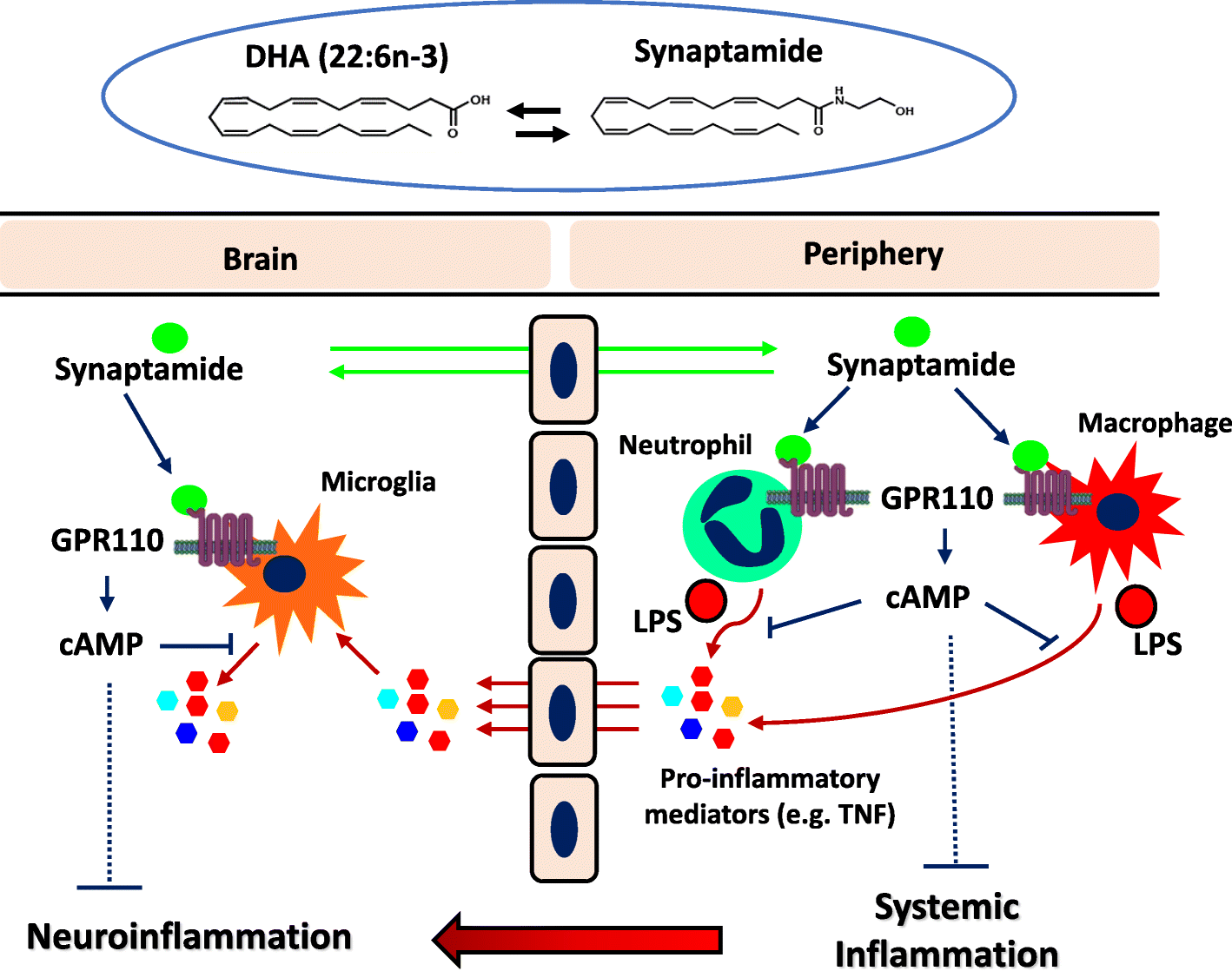
GPR110 (ADGRF1) mediates anti-inflammatory effects of N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text
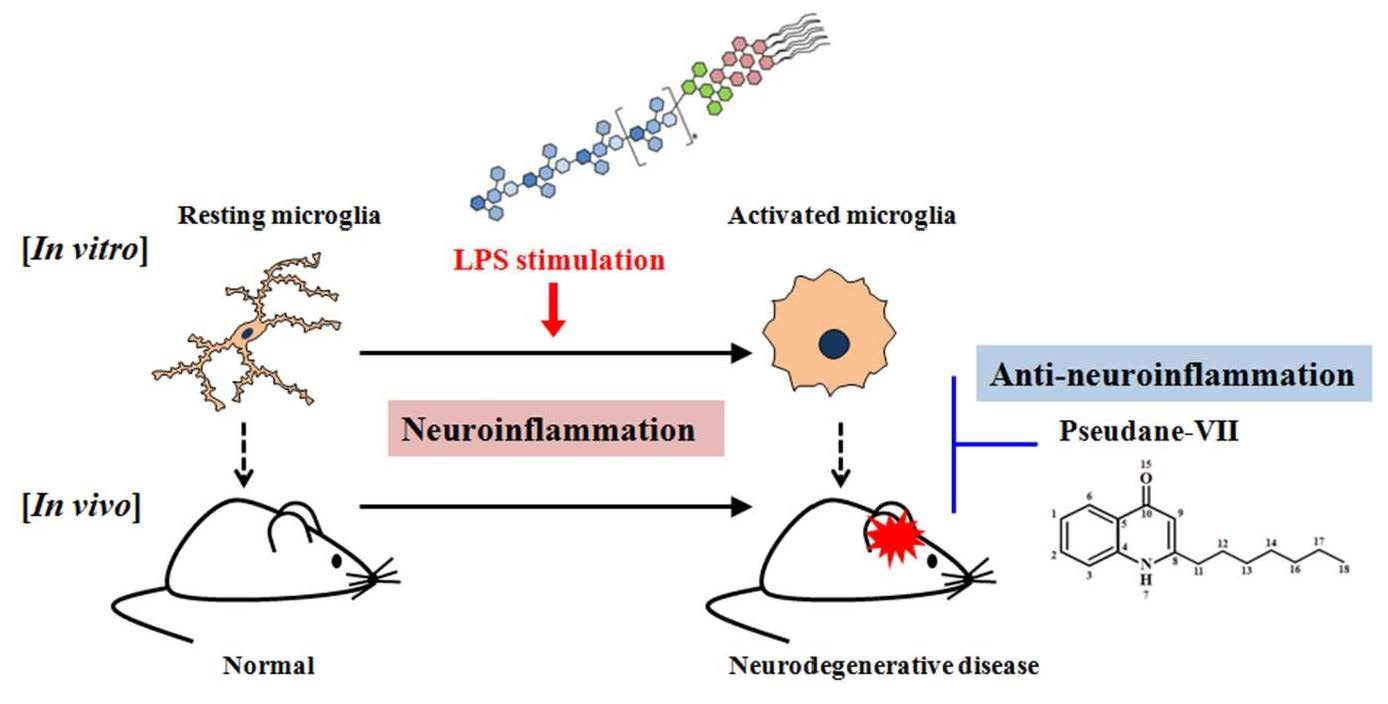
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Pseudane-VII Regulates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in Brain Microglia Cells through the Inhibition of iNOS Expression

Omarigliptin Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation and Dysfunction of the Integrity of the Blood–Brain Barrier | ACS Chemical Neuroscience
Ipriflavone and Ipriflavone loaded albumin nanoparticles reverse lipopolysaccharide induced neuroinflammation in rats | PLOS ONE
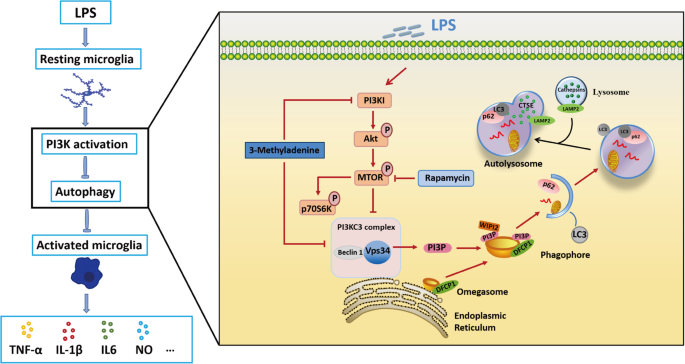
Lipopolysaccharide induces neuroinflammation in microglia by activating the MTOR pathway and downregulating Vps34 to inhibit autophagosome formation | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text
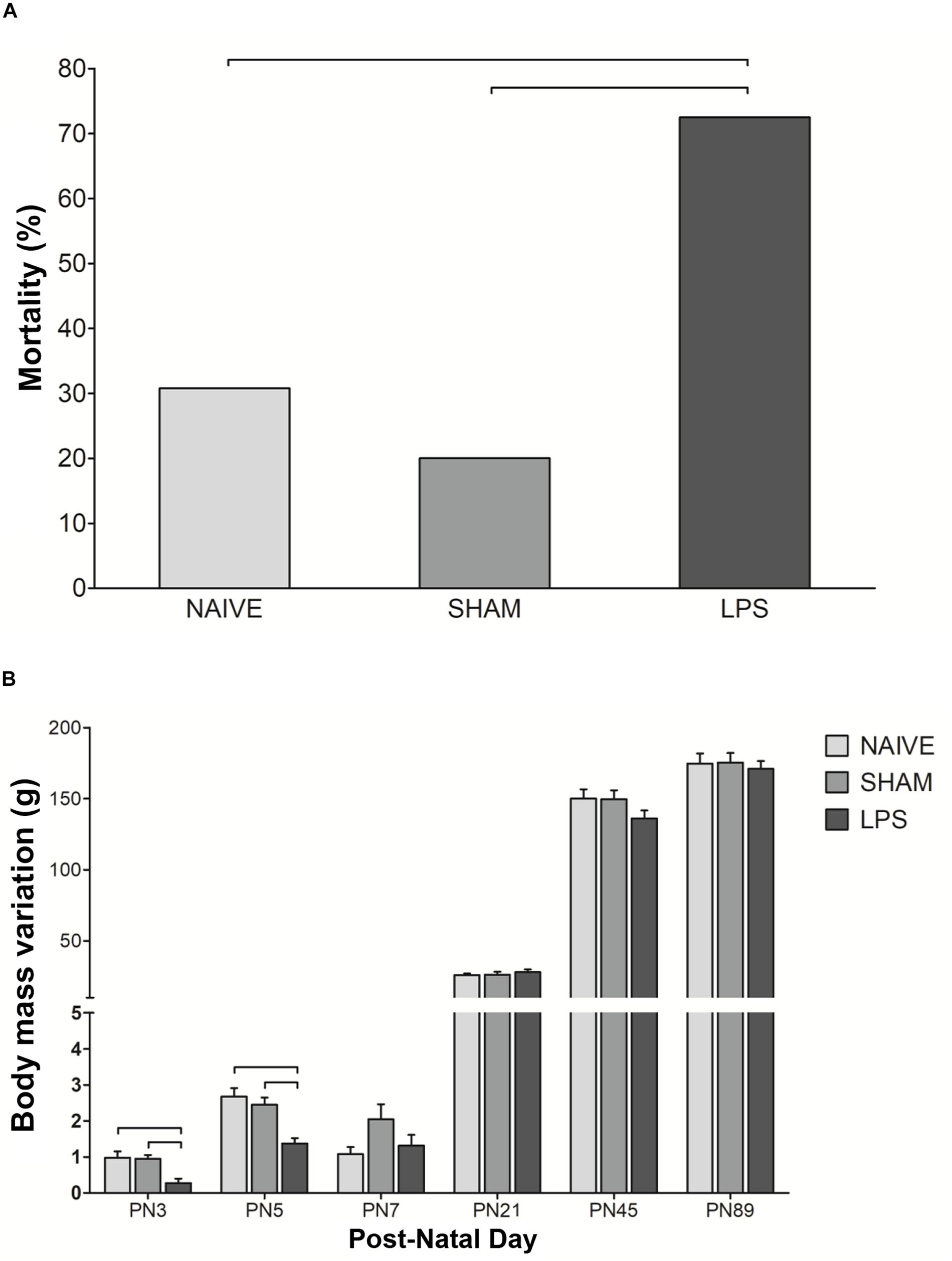
Frontiers | Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Systemic Inflammation in the Neonatal Period Increases Microglial Density and Oxidative Stress in the Cerebellum of Adult Rats